Understanding Key Players in Your Network: A Guide to Leveraging Network Influencers, Brokers, and Information Exchangers
PARTNER CPRM automatically identifies four key players in your network using four different centrality measures: Network Influencers, Out-fluencers, Network Brokers, and Information Exchangers. Each plays a unique role in how collaboration, trust, and resource-sharing function across your network. Understanding these roles can help you strategically strengthen relationships and optimize your network’s impact.
A Guide to Leveraging Network Key Player Relationships
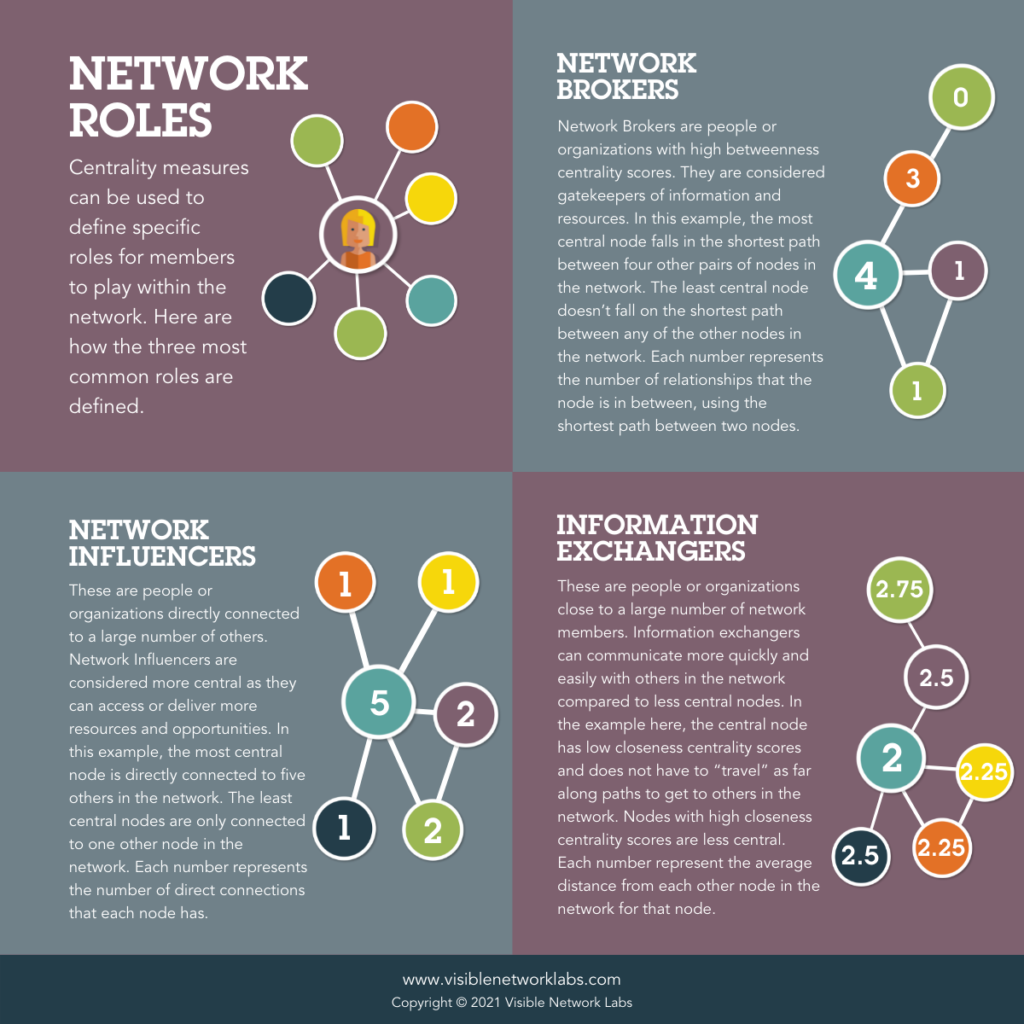
There are four types of key players identified using in-degree, out-degree, closeness, and betweenness centrality. You can use automated key player analysis or visualize these centrality scores directly using node sizing and explore the raw data in the network scores module.
1. Network Influencers (High In-Degree Centrality)
What It Means:
- Definition: Organizations or individuals who are frequently chosen
by others in the network as connections. - Role in the Network: These entities are perceived as highly valuable or influential because many others want to collaborate with them.
- Unique Value: Trusted hubs of knowledge, decision-making, and leadership. They shape opinions and can mobilize resources effectively.
Action Steps to Leverage Network In-fluencers:
✔ Engage Them in Decision-Making: Since they are seen as important, involving them in strategic planning ensures broader network buy-in.
✔ Encourage Knowledge Sharing: Use their influence to distribute critical information efficiently across the network.
✔ Monitor Power Dynamics: Avoid over-reliance on a few key influencers; ensure others also have pathways to contribute.
✔ Support Their Capacity: If they are overloaded with connections, offer resources or support to help them maintain their effectiveness.
2. Network Outfluencers (High Out-Degree Centrality)
What It Means:
- Definition: Organizations or individuals that initiate many connections with others in the network.
- Role in the Network: These are the proactive actors who seek information, partnerships, and collaborations.
- Unique Value: They are often highly engaged, innovative, and connected to many different network members, helping to facilitate outreach and partnership-building.
Action Steps to Leverage Network Out-fluencers:
✔ Empower Them as Network Catalysts: Use them to engage new or peripheral members, since they actively seek connections.
✔ Channel Their Energy into Outreach: They can help recruit new members, facilitate discussions, and spread best practices.
✔ Ensure Their Needs Are Met: Because they reach out to so many, they might require more support or resources to maintain effective collaborations.
✔ Encourage Balanced Collaboration: Since they initiate many relationships, ensure they also contribute to maintaining and deepening them over time.
3. Relationship Brokers (High Betweenness Centrality)
What It Means:
- Definition: Organizations or individuals who serve as bridges between different parts of the network, connecting groups that wouldn’t otherwise be linked.
- Role in the Network: They facilitate knowledge transfer and collaboration across silos. Removing them could fragment the network.
- Unique Value: They increase efficiency by reducing bottlenecks and improving connectivity between different stakeholders.
Action Steps to Leverage Relationship Brokers:
✔ Position Them as Connectors: Encourage them to play active roles in cross-sector initiatives or collaborative decision-making.
✔ Develop Redundancy in Connections: If a broker leaves, ensure other pathways exist so collaboration is not disrupted.
✔ Encourage Sharing of Knowledge: Since they connect different groups, they are great conduits for disseminating innovations or best practices.
✔ Support Their Role in Conflict Resolution: Because they bridge gaps, they may be effective mediators in disputes or misalignments within the network.
4. Information Exchangers (High Closeness Centrality)
What It Means:
- Definition: Organizations or individuals that can quickly reach and be reached by others in the network, minimizing the number of steps needed to transfer information.
- Role in the Network: They serve as key conduits for efficient communication.
- Unique Value: They facilitate fast decision-making and ensure that critical information reaches the right places at the right time.
Action Steps to Leverage Information Exchangers:
✔ Use Them for Rapid Communication: They can be leveraged to quickly disseminate key updates or emergency information.
✔ Engage Them in Feedback Loops: Since they can access many parts of the network quickly, they can help gather insights and relay responses effectively.
✔ Monitor Their Workload: Being central to communication can be overwhelming—ensure they have the capacity to manage their role.
✔ Integrate Them into Strategic Planning: Their broad connectivity allows them to see patterns across the network, making them valuable in identifying trends and opportunities.
Related Articles
Automated Key Player Analysis - Pro Feature
Automated Key Player Analysis helps identify three types of network members based on different types of centrality scores: degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and closeness centrality. This article explains how to access and use automated key ...Understanding your CPRM Account
PARTNER CPRM™ Key Terms PARTNER is built using network science and social network analysis principles and methods that aren't always obvious. Getting familiar with some common terms and concepts is a good first step to get to know the PARTNER CPRM ...Edit Relationship Settings for Network Maps
PARTNER CPRM includes multiple ways to visualize and color your relationships (lines) based on their relationship data. This allows you to layer multiple types of data to identify patterns and outliers across your network. For example, you can color ...How to Assess Relationship Intensity
Next, you can consider the quality of connections in your network by assessing the intensity of your relationships. Our relationship-intensity scale ranges from simple awareness of each other to full integration. The emphasis is not on the frequency ...Highlight Nodes in Your Network Maps
PARTNER CPRM now allows you to highlight individual nodes in your network maps to draw attention to specific members or patterns in your network. This can help emphasize key partners, track engagement over time, or simply make your network ...